 Display
- New in Rhino 5
Display
- New in Rhino 5
Overview
The Rhino 5 goals included
- Speed improvements
- Quick viewport display configuration
- Working display modes expanded and enhanced
- Presentation and rendered display modes expanded and enhanced
- Display mode plug-in support enhanced
Plus many other improvements, including draw order support, two‑point perspective, and enhanced clipping planes.
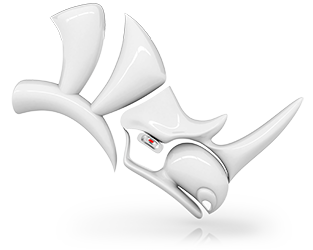
Display Modes
New modes
- Technical - Uses the new real-time silhouettes, with optional display of hidden lines, intersections, creases, seams, and shadows to simulate the look of a technical drawing. Objects behind other objects are occluded.
- Artistic - A variant of Technical mode, uses an image background and soft lines to create a pencil drawing effect suitable for concept review and illustrations.
- Pen - A variant of Technical mode, simulates the look of a simple pen drawing useful for schematic and instructional illustrations.
- Custom - As a user you can configure your own display modes. Here are some examples...
Enhanced
- Shaded Mode default material includes a subtle environment map and some gloss to better shape vizualization.
- Shadows are now an option
with settings for:
- Video memory usage
- Soft-edge quality
- Edge blurring
- Self-shadowing artifacts
- Transparent objects
- Camera-based clipping bubble
- Shadow color
- Dynamic display - An option to display bounding boxes instead of objects during view changes.
- Most display modes now support
the settings from the renderer, including:
- Lighting options with shadows in real-time including skylight
- Backgrounds and environments
- Ground plane
- Decals
- Bump mapping
- Complex materials including 2‑D and 3‑D procedural textures
- HDRi textures
- Multi-channel texture mapping
- All the texture mapping options including cube, horizontal cube, vertical cube, and equirectangular mapping
- Visibility options:
- Show clipping planes
- Show points
- Show pointclouds
- Nonmanifold edge display settings
- Shaded vertex colors for analysis results display.
- Isocurves - Optionally can have separate colors in the u‑ and v‑direction.
- A new No lighting option allows cartoon-style display.
- Clipped objects display
options:
- Fill solid areas with a specified solid color, the object color, clipping plane's material, or object rendering material.
- Show edges using the clipping plane's specified solid color or a specific color.
- Clip selection highlight wires.
- Advanced GPU Lighting - Takes advantage of high‑end graphic processors to provide better quality viewport display.
- Pipeline and conduit settings help provide compatibility with older graphics processors and drivers.
New
- Display Properties panel - Provides quick access to the most commonly used options.
- Draw Order provides control over which 2-D curve, text,
dimension, or hatch is drawn in front of
another. The new commands are:
- BringForward
- BringToFront
- ClearDrawOrder
- SendBackWard
- SendToBack
- DisableClippingPlane - Turns off selected clipping planes in the active viewport.
- EnableClippingPlane - Turns on selected clipping planes in the active viewport.
- Isometric - Changes the current viewport properties to a parallel projection isometric view looking from a specified quadrant toward 0,0.
- Two-point perspective is now supported in viewports and rendering.
- Options > View: New Auto adjust camera target after Pan and Zoom option. When on, the view depth adjusts in an attempt to keep the view rotation in a logical location related to the objects.
- ViewportTabs - Displays a tab control UI along the viewport edge. Viewport tabs are useful for managing multiple-page layout style viewports along with standard modeling viewports.
Enhancements
- Speed - Rhino 5 takes more advantage of graphics co-processors.
- BackgroundBitmap - The new 1to1 option uses the image resolution and DPI to automatically scale the image.
- Clipping Plane widget
- Show/Hide option
- Highlight selected clipping plane display controls for color and transparency
- Select clipped viewports in the Properties tab
- Dynamic section/fill display while moving the widget
- NewFloatingViewport
- Automatically copies the active view projection by default..
- The projection can be set to a NamedView.
- Dragging and dropping a viewport outside the Rhino viewport area creates a new floating viewport.
- -Hide/-Show - the command-line versions prompt to name the set of objects to hide or show.
- Named Views:
- The new widget interface can be used to place or edit the camera and target location and to set the field of view.
- Named views widget can be locked.
- A named view can be edited in a temporary floating viewport using the widget.
- The NamedView command displays a docking tabbed dialog box.
- A new option animates the view changes when a named view is restored.
- Pan:
- Press Shift to lock mouse panning to horizontal or vertical after the panning has started.
- The middle-mouse button can now be customized to emulate view manipulation in other software.
- Arrow key behavior - Arrow keys now always pan in plan view parallel viewports instead of rotating the view, preventing accidental rotation of the view.
- Rotate view - Ctrl+Shift+RMB now rotates perspective views around the pickpoint. The pickpoint can only be on things that are selectable, so, for example, locked objects and objects with points on are ignored.
- -ViewCaptureToFile
- A new Transparent background option has been added to the scripting (dashed) version.
- Scale option added to the dash version scales the image from the viewport size.
- Anti-aliasing enhanced with controls in Rhino.
- Display accuracy improved for objects very far from the origin.
- Indicator u and v arrows show the surface u‑ and v‑directions as needed in many commands.
- OptionsImport and OptionsExport - Includes display mode settings.
- Editing display modes:
- Display modes that have been changed from the default settings are highlighted in blue.
- Changes are displayed the viewports in real time.